How Computers Repreesent Data
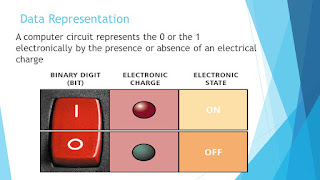
Computers are made of digital electronics circuity. And electronic circuits can exist either in ON or OFF state. Most of the electronics components of a computer use voltage levels to indicate their present state. For example, a transistor with five volts would be considered ON, while a transistor with no voltage would be considered OFF, CD-ROM's , for example, use microscopic dark spots on the surface of the disk to indicate OFF, while the ordinary shiny surface is considered ON. Hard disks use magnetism, where the magnetized spot is considered ON, while non-magnetized spots on the disk indicate OFF.
Computers are made of digital electronics circuity. And electronic circuits can exist either in ON or OFF state. Most of the electronics components of a computer use voltage levels to indicate their present state. For example, a transistor with five volts would be considered ON, while a transistor with no voltage would be considered OFF, CD-ROM's , for example, use microscopic dark spots on the surface of the disk to indicate OFF, while the ordinary shiny surface is considered ON. Hard disks use magnetism, where the magnetized spot is considered ON, while non-magnetized spots on the disk indicate OFF.
These patterns of ON and OFF stored inside the computer are used to encode numbers using the binary number system. The binary number system is a method of storing ordinary numbers such as 34 or 456 or text data such as names as patterns of 1 's and 0 's . Because of their digital nature, a computer's electronics circuitry can easily manipulate numbers stored in binary by treating 1 as ON and 0 as OFF. Computers have circuits that can add, subtract multiply , divide, and do so many other things to numbers stored in binary form.

No comments:
Post a Comment